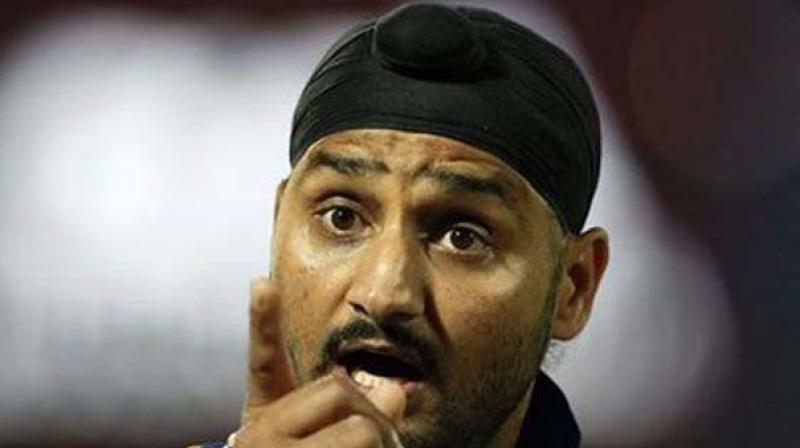
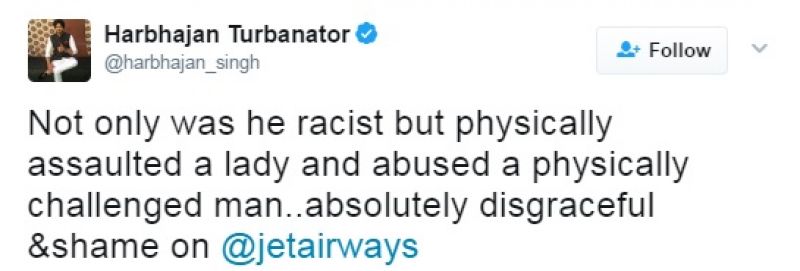
Francis Xavier : A Saint or Ruthless Father
of Bloodiest Inquisition in Goa
Margashirsha Shukla 9, Kaliyug Varsha 5113
https://www.hindujagruti.org/hindu-issues/hatkatro-khaamb/francis-xavier
We can see what was St. Francis Xavier’s first priority in India through his own words ‘I want to free the poor Hindus from the stranglehold of the Brahmins and destroy the places where evil spirits are worshipped. The Brahmins are the most perverse people in the world…. They never tell the truth, but think of nothing but how to tell subtle lies and to receive the simple and ignorant people… They are as perverse and wicked a set as can anywhere be found, and to whom applies the Psalm, which says: ‘From an unholy race, and wicked and crafty men, deliver me, Lord’. The poor people do exactly what the Brahmins tell them…. If there were no Brahmins in the area, all Hindus would accept conversion to our faith’.
St. Francis Xavier wrote a letter to the Society of Jesus in which he said, ‘Following the Baptisms, the new Christians return to their homes and come back with their wives and families to be in their turn also prepared for Baptism. After all have been baptised, I order that everywhere the temples of the false Gods be pulled down and idols broken. I KNOW NOT HOW TO DESCRIBE IN WORDS THE JOY THAT I FEEL BEFORE THE SPECTACLE OF PULLING DOWN AND DESTROYING THE IDOLS BY THE VERY PEOPLE WHO FORMERLY WORSHIPPED THEM’.
St. Francis Xavier did this in Quilon after the Hindu Raja of Quilon had given him a munificently large grant of land and other resources to build Churches in his territory. After taking this grant, St. Xavier converted Hindus into Christianity. After doing that he said that he was in a state of ecstatic joy! The same kind of savage joy was expressed by another equally savage temple destroyer Mughal Emperor called Aurangazeb who ruled from 1658 to 1707. So much for terrorist Christianity and terrorist Islam! So much for peace-loving and compassionate Christianity and Islam! So much for Christian Brotherhood and Islamic Brotherhood!
No wonder the great German philosopher Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche [1844 –1900], not belonging to the VHP or RSS or Sangh Pariwar(!) paid this legitimate tribute to ever-compassionate Christianity: ‘I call Christianity the one great curse of enormous and innermost perversion, the one great instinct of revenge, for which no means are venomous, too underhand, too underground and too petty—I call it the one immortal blemish of mankind’. I am sure the Pope in Rome will take immediate action to ex-communicate Nietzsche, posthumously, for his above Paganish and Heathenish indiscretion, taking the ever-obliging Sonia-directed Pro-Catholic UPA Government into private confidence! Our Prime Minister has prepared the ground for this drama by his recent statement on the mass Hindu Rebellion in Orissa.
In these columns yesterday (30-8-08) I had written about the atrocities committed by St. Francis Xavier and his disciples against the Hindus of Goa in the 16th century. Aided by guided and frenzied mobs, he and his missionaries did not lag behind the Islamic iconoclastic zeal of Mohammad of Ghazni in the 11th century, Malik-a-fur and Timur in the 14th century. They destroyed thousands of Hindu temples and non-Christian places of worship in South India in general and Goa in particular.
Even before the arrival of St. Francis Xavier in Goa in 1542, two Portuguese Governors called Minguet Vaz and Diago Borba, inaugurated the State-sponsored movement for the demolition of the Hindu temples and other vestiges of Hindu religion. Most of the temples of Goa, Divar, Chorada and Jua region were destroyed in 1540. In 1541 a policy of ‘Regour of Mercy’ was announced as the main plank of anti-Hindu policy to be followed by the government in Goa.
In this year, after the demolition of temples, various leaders of the Hindu community were terrorised into submission and made to agree of, ‘Their free volition that the income of the lands belonging to the ancient Hindu temples which had been destroyed might be applied to the upkeep of Christian Churches and Christian Missionaries…. It was also resolved that the income should, in future, be applied towards and donated to the Chapels built in this island and also to defray the expenses of the confraternity of the converts to the faith. As a result of this declared ‘Anti-Hindu and Hindu Extermination Policy’ (like that of the Catholic Sonia-directed UPA surrogate government of India today!!), the St. Paul’s College was established and maintained out of the income of the Hindu temples which had been destroyed’.
After the arrival of St. Francis Xavier in 1542, the movement for temple demolition in Goa was further accelerated, as he was an instigator and a role model for the demolition of the Hindu temples. From then on, the Jesuits did their worst under his cruel leadership, using every form of bribery, threat and torture against the Hindus to effect a conversion! He noticed that though some Hindus, baptised earlier through force and fraud, were still secretly worshipping these ‘evil spirits’.
Enraged by this ‘paganish and heathenish barbarism’, St. Francis Xavier reacted strongly with Christian compassion and understanding marked by unsurpassed nobility. According to the ‘History of Christianity in India’, his reaction was: ‘When the boys informed him that some had made an idol, he went with them and had it broken into a thousand pieces. If in spite of all his Divine advice someone persisted in making idols, he would have them punished by the Patingatis (Heads of Parava Village) are banished to another village. One day when he heard that idols had been worshipped in the house of a Christian, he ordered the hut to be burnt down as a warning to others (Source-Silva Rego Vol.I Page 158)’.
Regarding St.Francis Xavier’s way of ‘violent evangelism’, Hector has written: ‘In the matter of conversion, Xavier held exceedingly crude ideas. His great aim was to get hold of the younger portion of the population… Xavier is said to have baptised seven hundred thousand natives, whom he left as ignorant as he found them. His motto seems to have been quantity and not quality’.
P.B.Cunha, a Goan freedom fighter and eminent writer has been very critical of Xavier’s method of evangelism. To quote his words: ‘That Saint (Xavier) came as a missionary with the patronage and protection of the Portuguese King and used his power of proselytisation to further the Portuguese Imperial designs’.
In order to promote conversions and create an atmosphere of mental terror, St. Francis Xavier and his missionaries saw to it that the Hindus were tortured by all possible means, particularly where the evidence against the accused (foisted cases for Inquisition and Conversion through fraud, force and inducement!) was incomplete, defective or conflicting. I have presented above the pictures/photographs of the tools, implements and other appliances carefully designed by St. Francis Xavier and his missionaries for the human and humane conversion of the Hindus of Goa through organized torture, fully backed by the might of the Portuguese State in the 16th century.
We can see that there were specially designed sharp instruments with spikes for cutting the ears of Hindus, for breaking their legs and shin, for disembowelling them over the rack, for breaking their jaws, for tearing their tongues and finally there was a specially designed Christian equipment (designed with Christian compassion of rigorous mercy!) for tearing apart the female breasts! I acknowledge my debt to Shri Maanoj Rakhit, a great Hindutva scholar from Bombay for helping me with the above rare photographs of the implements and tools of Christian torture in Goa during the days of the Holy Inquisition!
Very unfortunately thousands of Hindus who were tortured and killed by St. Francis Xavier and his missionaries have not left behind contemporary records relating to their sufferings, trials and tribulations. One of the most authentic records relating to the Holy Inquisition in Goa was left behind by a French Jewish Doctor called Dellon. About him, the savant Ferdinand Denis wrote: ‘Many voyagers painted with great energy the torments which the inquisition of Goa inflicted on its prisoners, but the most minute report, without contradiction and the most moderate in all respects was that of a French doctor called Dellon, who wrote a special treatise on this tribunal, of which he was one of the victims’.
Indeed a young French Doctor by the name of Dellon, ten years after he escaped from his punishment in the galleys in Lisbon in 1677, wrote the famous book ‘RELATION DE L’INQUISITION DE GOA’, printed in Holland in 1687. The acquisition of Dellon’s book was most difficult for more than two hundred years, because not only it was antique but prohibited. Only Mr.Cunha Rivara, in the late 19th century, on the way to serve as Secretary to the Governor in Goa, was able to get a copy from the curator of the Public Library in Lisbon, Joƒo Jos, Barbosa.
From Dr.Dellon’s classic book referred to above, we get the following details relating to the Holy Inquisition in Goa. The House of Inquisition (Divine Torments!) of Hindus was a subterranean grotto, so that others might not hear the cries of the wretched. Many a time, the Hindu victims died under torture; their bodies were interred within the compound, and the bones were exhumed for the auto da fe, and burnt in public. Those Hindus who were branded as convicts, and persisted in denying the facts of which they were accused, or who were relapsed, were obliged to wear another scapulary which was called Samarra, a brown cloth, on which the portrait of the victim was painted above flames, and surrounded by demons. Below this portrait were written down the name of the condemned and the crimes. But for those who accused themselves, after the sentence was pronounced, and who were not relapsed, a different Samarra was given: in these brown vests the flames were facing downwards, which was called ‘fogo revolto’.
After the distribution of the Sambenitos, five pointed bonnets or mitres of cardboard, all painted with demons and flames, and the word ‘feiticeiro’ (sorcerer) were brought and placed on the heads of the persons accused of necromancy. Standing up all night, at last at 5.30 a.m. the sun rose, and the bell of the cathedral started tolling. This was the signal for the population of Goa to wake up, and come to witness the august ceremony of the auto da fe, which was considered as a triumph of the Holy Office.
By daylight, each convict was ordered to march alongside a godfather, one of the officials assigned to each victim. It was a great honour to be appointed godfather for these ceremonies. Finally, covered with shame and confusion, tired of the long march, the condemned reached the church of St. Francis, which was decked with great pomp and circumstance. The altar was covered with black cloth on which stood six silver candleholders. On both sides of the altar there were two kinds of thrones: the right side for the inquisitor and his councillors, and the left side for the viceroy and his court. The convicts and godfathers were seated on benches. Once the sermon was concluded, two officials went up to the pulpit, to read publicly the proceedings of all the guilty, and to declare the sentences upon them. Generally all the Hindu victims were either put to death in all kinds of barbarous ways.
Mr. Alfred Demersay, French commissioner in Portugal and Spain in 1862, on examining the archives of Lisbon where past processes of inquisition were kept, wrote: ‘Only the Inquisition has furnished 40,000 proceedings of lawsuits, which are the most precious elements to write the history of this nefarious institution, and an inexhaustible mine for the novelists and authors of melodramas. The inquisition was the greatest terror of our ancestors in Goa because of its incredible tyranny; it was an independent terrorist Republic, which did not recognise even the Viceroys as their superiors’.
How immoral and barbarous were the Holy Inquisitors in Goa (who took hourly instructions from St. Francis Xavier from 1542 to 1551) in the 16th century can be seen by the oration given by Archbishop of Evora at the Cathedral Church of Lisbon in June 1897: ‘The Inquisition was an infamous TRIBUNAL at all places. But the infamy never reached greater depths, nor was more vile, more black, and more completely determined by mundane interests than at the TRIBUNAL OF GOA, by irony called the HOLY OFFICE. Here the Inquisitors went to the length of imprisoning in its jails women who resisted their advances, and after having satisfied their bestial instincts there, ordering that they be burnt as heretics’. (Source The Hindus and the Portuguese Republic, Priolkar Page 174 – 175).
‘When I think of all the harm the Bible has done, I despair of ever writing anything to equal it’
— Oscar Wilde (1854-1900), Irish author:
In order to accelerate the process of Christianising of the Hindus and the demolition of Hindu temples, one of the associates of St. Francis Xavier, Minguel Vaz, the then Vicar General of India appointed by the Pope in Rome, requested the King of Portugal as part of his 41 Point Programme to destroy all Hindu Temples in October 1546 as follows: ‘Since idolatry is so great and offence against God, as is manifest to all, it is just that Your Majesty should not permit it within your territories, and an order should be promulgated in Goa to the effect that in the whole island there should not be any temple public or secret. Contravention thereof should entail grave penalties that no Hindu should make idols in any form, neither of stone, nor of wood, nor of copper, nor of any other metal…. and that persons who are in charge of St. Paul’s should have the power to search the houses of the Brahmins and other Hindus, in case there exists a presumption or suspicion of the idols there’.
Consequently on March 8, 1547, the King of Portugal ordered his Viceroy at Goa that all the Hindu temples should be destroyed forthwith. Minguel Vaz even before the receipt of this formal order had commenced the operation of destruction of Hindu temples. Consequently there was a Hindu uprising and the Hindus succeeded in poisoning him to death. Following the example of Minguel Vaz, similar orders for destruction of Hindu temples were issued by Viceroy D. Antao de Noronha on 29 August 1556.
In March 1569, an order was promulgated by which, the income of the Hindu temples of Bardez and Salsete, which had been destroyed by the Jesuits, was transferred to Christian Churches. The Hindu inhabitants of that region were called and asked to disclose under Oath ‘information’ about the properties attached to the temples and upon their due compliance with this order, the entire temple properties were transferred to the Churches (Source: A K Priolkar – The Goa Inquisition, page no.85). At many places the temples were destroyed and the Churches were built in those places. Thus we can see that the Jesuit Inquisitors in Goa were only following the path of Muslim marauders like Mohammed of Ghori, Allaudin Khilji, Babur and Aurangazeb. Babur built his Babri Masjid at the site that became available after his planned destruction of the Sri Ram Temple at Ayodhya in 1528.
Likewise, the Jesuits of Goa also erected Churches on destroyed temple sites in hundreds of places throughout Goa from 1560 to 1812. For example according to the Imperial Gazetteer of British India ‘The Church of Cortalim is erected on the same site where formerly the idol of Mangesh was worshipped by the Hindus. Some missionary records refer to many famous Hindu temples being converted into Churches at these places’. According to Sitaram Goel ‘A magnificent Hindu temple in the Elephanta Caves was turned into a Chapel’.
Throughout Portuguese Rule in Goa, various Viceregal and Church Council decrees banished the Hindu priests from the Portuguese territories. The public practice of Hindu rites including marriage rites was banned. Only Christians were preferred in public employment. The Government ensured that the Hindus would not harass those who became Christians; yet at the same time and to the contrary, the Hindus were forced to assemble periodically in Churches to listen to Christian preaching or to the refutation of the Hindu religion. Perhaps because of all these anti-Hindu acts, Mahatma Gandhi wrote very clearly in his autobiography ‘The Story of My Experiments with Truth’: ‘I had started disliking Christianity. This was not without any reason. Those days Christian missionaries used to stand in a corner near the High School in Rajkot and used disgraceful words against Hindus and their Gods/Goddesses. I could not bear this’. In fact not only Gandhiji, no self-respecting Hindu can bear this.
Immediately after the establishment of Portuguese Rule in Goa, a number of ANTI-HINDU LAWS were enacted, and most of them, during the period of Holy Inquisition in Goa from 1560 to 1812. What is worse, all of them were strictly and often ruthlessly implemented to punish the Hindus and more particularly theBrahmins.
On 3rd December, there is a fair of the so-called Saint Francis Xavier at Old Goa. Hindus also go to this fair and pray for curing of physical ailments. Lack of ‘Dharmashikshan’ among Hindus is the reason that they fall prey to such so-called miracles of so-called saints. We give below how this Xavier and under his order, the Portuguese oppressed Hindus.
By Mr. V. Sundaram :
St. Francis Xavier landed in Goa on 6 May 1542, with a resolve of ‘uprooting paganism’ from the soil of India and planting Christianity in its place. And so all plans of persecution and oppression of the Hindus came along with him. All religious policies and procedures of forcible and fraudulent conversions and demolitions of the Hindu Temples and idols were undertaken under his guidance and missionary zeal. Thus it was St.Francis Xavier who laid the foundation for the ‘compassionate’ (barbarous!) for an organised system of Holy Inquisition against the Hindus in Goa.
St.Francis Xavier was a pioneer of anti-Brahmanism, which was adopted later as a major plan in the missionary propaganda during British Rule as evident below. Lord Minto, the Governor General of India from 1807 to 1812, sent some propaganda material used by the English missionaries in India to British Parliament and in particular referred to one Christian Tract about which he said ‘the remainder of this Tract seems to aim principally at a general massacre and extermination of the Brahmins’.
St.Francis Xavier was a pioneer of anti-Brahmanism, which was adopted later as a major plan in the missionary propaganda during British Rule as evident below. Lord Minto, the Governor General of India from 1807 to 1812, sent some propaganda material used by the English missionaries in India to British Parliament and in particular referred to one Christian Tract about which he said ‘the remainder of this Tract seems to aim principally at a general massacre and extermination of the Brahmins’.
We can see what was St. Francis Xavier’s first priority in India through his own words ‘I want to free the poor Hindus from the stranglehold of the Brahmins and destroy the places where evil spirits are worshipped. The Brahmins are the most perverse people in the world…. They never tell the truth, but think of nothing but how to tell subtle lies and to receive the simple and ignorant people… They are as perverse and wicked a set as can anywhere be found, and to whom applies the Psalm, which says: ‘From an unholy race, and wicked and crafty men, deliver me, Lord’. The poor people do exactly what the Brahmins tell them…. If there were no Brahmins in the area, all Hindus would accept conversion to our faith’.
St. Francis Xavier wrote a letter to the Society of Jesus in which he said, ‘Following the Baptisms, the new Christians return to their homes and come back with their wives and families to be in their turn also prepared for Baptism. After all have been baptised, I order that everywhere the temples of the false Gods be pulled down and idols broken. I KNOW NOT HOW TO DESCRIBE IN WORDS THE JOY THAT I FEEL BEFORE THE SPECTACLE OF PULLING DOWN AND DESTROYING THE IDOLS BY THE VERY PEOPLE WHO FORMERLY WORSHIPPED THEM’.
St. Francis Xavier did this in Quilon after the Hindu Raja of Quilon had given him a munificently large grant of land and other resources to build Churches in his territory. After taking this grant, St. Xavier converted Hindus into Christianity. After doing that he said that he was in a state of ecstatic joy! The same kind of savage joy was expressed by another equally savage temple destroyer Mughal Emperor called Aurangazeb who ruled from 1658 to 1707. So much for terrorist Christianity and terrorist Islam! So much for peace-loving and compassionate Christianity and Islam! So much for Christian Brotherhood and Islamic Brotherhood!
No wonder the great German philosopher Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche [1844 –1900], not belonging to the VHP or RSS or Sangh Pariwar(!) paid this legitimate tribute to ever-compassionate Christianity: ‘I call Christianity the one great curse of enormous and innermost perversion, the one great instinct of revenge, for which no means are venomous, too underhand, too underground and too petty—I call it the one immortal blemish of mankind’. I am sure the Pope in Rome will take immediate action to ex-communicate Nietzsche, posthumously, for his above Paganish and Heathenish indiscretion, taking the ever-obliging Sonia-directed Pro-Catholic UPA Government into private confidence! Our Prime Minister has prepared the ground for this drama by his recent statement on the mass Hindu Rebellion in Orissa.
In these columns yesterday (30-8-08) I had written about the atrocities committed by St. Francis Xavier and his disciples against the Hindus of Goa in the 16th century. Aided by guided and frenzied mobs, he and his missionaries did not lag behind the Islamic iconoclastic zeal of Mohammad of Ghazni in the 11th century, Malik-a-fur and Timur in the 14th century. They destroyed thousands of Hindu temples and non-Christian places of worship in South India in general and Goa in particular.
Even before the arrival of St. Francis Xavier in Goa in 1542, two Portuguese Governors called Minguet Vaz and Diago Borba, inaugurated the State-sponsored movement for the demolition of the Hindu temples and other vestiges of Hindu religion. Most of the temples of Goa, Divar, Chorada and Jua region were destroyed in 1540. In 1541 a policy of ‘Regour of Mercy’ was announced as the main plank of anti-Hindu policy to be followed by the government in Goa.
In this year, after the demolition of temples, various leaders of the Hindu community were terrorised into submission and made to agree of, ‘Their free volition that the income of the lands belonging to the ancient Hindu temples which had been destroyed might be applied to the upkeep of Christian Churches and Christian Missionaries…. It was also resolved that the income should, in future, be applied towards and donated to the Chapels built in this island and also to defray the expenses of the confraternity of the converts to the faith. As a result of this declared ‘Anti-Hindu and Hindu Extermination Policy’ (like that of the Catholic Sonia-directed UPA surrogate government of India today!!), the St. Paul’s College was established and maintained out of the income of the Hindu temples which had been destroyed’.
After the arrival of St. Francis Xavier in 1542, the movement for temple demolition in Goa was further accelerated, as he was an instigator and a role model for the demolition of the Hindu temples. From then on, the Jesuits did their worst under his cruel leadership, using every form of bribery, threat and torture against the Hindus to effect a conversion! He noticed that though some Hindus, baptised earlier through force and fraud, were still secretly worshipping these ‘evil spirits’.
Enraged by this ‘paganish and heathenish barbarism’, St. Francis Xavier reacted strongly with Christian compassion and understanding marked by unsurpassed nobility. According to the ‘History of Christianity in India’, his reaction was: ‘When the boys informed him that some had made an idol, he went with them and had it broken into a thousand pieces. If in spite of all his Divine advice someone persisted in making idols, he would have them punished by the Patingatis (Heads of Parava Village) are banished to another village. One day when he heard that idols had been worshipped in the house of a Christian, he ordered the hut to be burnt down as a warning to others (Source-Silva Rego Vol.I Page 158)’.
Regarding St.Francis Xavier’s way of ‘violent evangelism’, Hector has written: ‘In the matter of conversion, Xavier held exceedingly crude ideas. His great aim was to get hold of the younger portion of the population… Xavier is said to have baptised seven hundred thousand natives, whom he left as ignorant as he found them. His motto seems to have been quantity and not quality’.
P.B.Cunha, a Goan freedom fighter and eminent writer has been very critical of Xavier’s method of evangelism. To quote his words: ‘That Saint (Xavier) came as a missionary with the patronage and protection of the Portuguese King and used his power of proselytisation to further the Portuguese Imperial designs’.
In order to promote conversions and create an atmosphere of mental terror, St. Francis Xavier and his missionaries saw to it that the Hindus were tortured by all possible means, particularly where the evidence against the accused (foisted cases for Inquisition and Conversion through fraud, force and inducement!) was incomplete, defective or conflicting. I have presented above the pictures/photographs of the tools, implements and other appliances carefully designed by St. Francis Xavier and his missionaries for the human and humane conversion of the Hindus of Goa through organized torture, fully backed by the might of the Portuguese State in the 16th century.
We can see that there were specially designed sharp instruments with spikes for cutting the ears of Hindus, for breaking their legs and shin, for disembowelling them over the rack, for breaking their jaws, for tearing their tongues and finally there was a specially designed Christian equipment (designed with Christian compassion of rigorous mercy!) for tearing apart the female breasts! I acknowledge my debt to Shri Maanoj Rakhit, a great Hindutva scholar from Bombay for helping me with the above rare photographs of the implements and tools of Christian torture in Goa during the days of the Holy Inquisition!
Very unfortunately thousands of Hindus who were tortured and killed by St. Francis Xavier and his missionaries have not left behind contemporary records relating to their sufferings, trials and tribulations. One of the most authentic records relating to the Holy Inquisition in Goa was left behind by a French Jewish Doctor called Dellon. About him, the savant Ferdinand Denis wrote: ‘Many voyagers painted with great energy the torments which the inquisition of Goa inflicted on its prisoners, but the most minute report, without contradiction and the most moderate in all respects was that of a French doctor called Dellon, who wrote a special treatise on this tribunal, of which he was one of the victims’.
Indeed a young French Doctor by the name of Dellon, ten years after he escaped from his punishment in the galleys in Lisbon in 1677, wrote the famous book ‘RELATION DE L’INQUISITION DE GOA’, printed in Holland in 1687. The acquisition of Dellon’s book was most difficult for more than two hundred years, because not only it was antique but prohibited. Only Mr.Cunha Rivara, in the late 19th century, on the way to serve as Secretary to the Governor in Goa, was able to get a copy from the curator of the Public Library in Lisbon, Joƒo Jos, Barbosa.
From Dr.Dellon’s classic book referred to above, we get the following details relating to the Holy Inquisition in Goa. The House of Inquisition (Divine Torments!) of Hindus was a subterranean grotto, so that others might not hear the cries of the wretched. Many a time, the Hindu victims died under torture; their bodies were interred within the compound, and the bones were exhumed for the auto da fe, and burnt in public. Those Hindus who were branded as convicts, and persisted in denying the facts of which they were accused, or who were relapsed, were obliged to wear another scapulary which was called Samarra, a brown cloth, on which the portrait of the victim was painted above flames, and surrounded by demons. Below this portrait were written down the name of the condemned and the crimes. But for those who accused themselves, after the sentence was pronounced, and who were not relapsed, a different Samarra was given: in these brown vests the flames were facing downwards, which was called ‘fogo revolto’.
After the distribution of the Sambenitos, five pointed bonnets or mitres of cardboard, all painted with demons and flames, and the word ‘feiticeiro’ (sorcerer) were brought and placed on the heads of the persons accused of necromancy. Standing up all night, at last at 5.30 a.m. the sun rose, and the bell of the cathedral started tolling. This was the signal for the population of Goa to wake up, and come to witness the august ceremony of the auto da fe, which was considered as a triumph of the Holy Office.
By daylight, each convict was ordered to march alongside a godfather, one of the officials assigned to each victim. It was a great honour to be appointed godfather for these ceremonies. Finally, covered with shame and confusion, tired of the long march, the condemned reached the church of St. Francis, which was decked with great pomp and circumstance. The altar was covered with black cloth on which stood six silver candleholders. On both sides of the altar there were two kinds of thrones: the right side for the inquisitor and his councillors, and the left side for the viceroy and his court. The convicts and godfathers were seated on benches. Once the sermon was concluded, two officials went up to the pulpit, to read publicly the proceedings of all the guilty, and to declare the sentences upon them. Generally all the Hindu victims were either put to death in all kinds of barbarous ways.
Mr. Alfred Demersay, French commissioner in Portugal and Spain in 1862, on examining the archives of Lisbon where past processes of inquisition were kept, wrote: ‘Only the Inquisition has furnished 40,000 proceedings of lawsuits, which are the most precious elements to write the history of this nefarious institution, and an inexhaustible mine for the novelists and authors of melodramas. The inquisition was the greatest terror of our ancestors in Goa because of its incredible tyranny; it was an independent terrorist Republic, which did not recognise even the Viceroys as their superiors’.
How immoral and barbarous were the Holy Inquisitors in Goa (who took hourly instructions from St. Francis Xavier from 1542 to 1551) in the 16th century can be seen by the oration given by Archbishop of Evora at the Cathedral Church of Lisbon in June 1897: ‘The Inquisition was an infamous TRIBUNAL at all places. But the infamy never reached greater depths, nor was more vile, more black, and more completely determined by mundane interests than at the TRIBUNAL OF GOA, by irony called the HOLY OFFICE. Here the Inquisitors went to the length of imprisoning in its jails women who resisted their advances, and after having satisfied their bestial instincts there, ordering that they be burnt as heretics’. (Source The Hindus and the Portuguese Republic, Priolkar Page 174 – 175).
‘When I think of all the harm the Bible has done, I despair of ever writing anything to equal it’
— Oscar Wilde (1854-1900), Irish author:
In order to accelerate the process of Christianising of the Hindus and the demolition of Hindu temples, one of the associates of St. Francis Xavier, Minguel Vaz, the then Vicar General of India appointed by the Pope in Rome, requested the King of Portugal as part of his 41 Point Programme to destroy all Hindu Temples in October 1546 as follows: ‘Since idolatry is so great and offence against God, as is manifest to all, it is just that Your Majesty should not permit it within your territories, and an order should be promulgated in Goa to the effect that in the whole island there should not be any temple public or secret. Contravention thereof should entail grave penalties that no Hindu should make idols in any form, neither of stone, nor of wood, nor of copper, nor of any other metal…. and that persons who are in charge of St. Paul’s should have the power to search the houses of the Brahmins and other Hindus, in case there exists a presumption or suspicion of the idols there’.
Consequently on March 8, 1547, the King of Portugal ordered his Viceroy at Goa that all the Hindu temples should be destroyed forthwith. Minguel Vaz even before the receipt of this formal order had commenced the operation of destruction of Hindu temples. Consequently there was a Hindu uprising and the Hindus succeeded in poisoning him to death. Following the example of Minguel Vaz, similar orders for destruction of Hindu temples were issued by Viceroy D. Antao de Noronha on 29 August 1556.
In March 1569, an order was promulgated by which, the income of the Hindu temples of Bardez and Salsete, which had been destroyed by the Jesuits, was transferred to Christian Churches. The Hindu inhabitants of that region were called and asked to disclose under Oath ‘information’ about the properties attached to the temples and upon their due compliance with this order, the entire temple properties were transferred to the Churches (Source: A K Priolkar – The Goa Inquisition, page no.85). At many places the temples were destroyed and the Churches were built in those places. Thus we can see that the Jesuit Inquisitors in Goa were only following the path of Muslim marauders like Mohammed of Ghori, Allaudin Khilji, Babur and Aurangazeb. Babur built his Babri Masjid at the site that became available after his planned destruction of the Sri Ram Temple at Ayodhya in 1528.
Likewise, the Jesuits of Goa also erected Churches on destroyed temple sites in hundreds of places throughout Goa from 1560 to 1812. For example according to the Imperial Gazetteer of British India ‘The Church of Cortalim is erected on the same site where formerly the idol of Mangesh was worshipped by the Hindus. Some missionary records refer to many famous Hindu temples being converted into Churches at these places’. According to Sitaram Goel ‘A magnificent Hindu temple in the Elephanta Caves was turned into a Chapel’.
Throughout Portuguese Rule in Goa, various Viceregal and Church Council decrees banished the Hindu priests from the Portuguese territories. The public practice of Hindu rites including marriage rites was banned. Only Christians were preferred in public employment. The Government ensured that the Hindus would not harass those who became Christians; yet at the same time and to the contrary, the Hindus were forced to assemble periodically in Churches to listen to Christian preaching or to the refutation of the Hindu religion. Perhaps because of all these anti-Hindu acts, Mahatma Gandhi wrote very clearly in his autobiography ‘The Story of My Experiments with Truth’: ‘I had started disliking Christianity. This was not without any reason. Those days Christian missionaries used to stand in a corner near the High School in Rajkot and used disgraceful words against Hindus and their Gods/Goddesses. I could not bear this’. In fact not only Gandhiji, no self-respecting Hindu can bear this.
Immediately after the establishment of Portuguese Rule in Goa, a number of ANTI-HINDU LAWS were enacted, and most of them, during the period of Holy Inquisition in Goa from 1560 to 1812. What is worse, all of them were strictly and often ruthlessly implemented to punish the Hindus and more particularly theBrahmins.
.jpg)